News
Center
News
Center
The role of "light" in film and television works, games, and virtual environments is very important. It is an important modeling method. It plays a role in conveying information, expressing emotions, accentuating the atmosphere, and portraying character and psychological changes in the film. It affects the formation of the film's tone and the presentation of the film's style, forms an opposing and unified relationship with the film's tone, and combines with other modeling methods to express the rhythm and melody of the film.
Many special effects scenes in film and television works need to be completed with the help of green screens. When the technology is not hard, the "five gross special effects" tragedies often occur.

It is even more difficult to reproduce the perfect light effect. With the evolution of computer vision technology, computers have been able to restore human face shapes and skin lines more "naturally", but they still lack a sense of realism in simulating lighting conditions.
And Google recently announced a new lighting-based technology-Relightables. Can solve this perfectly.
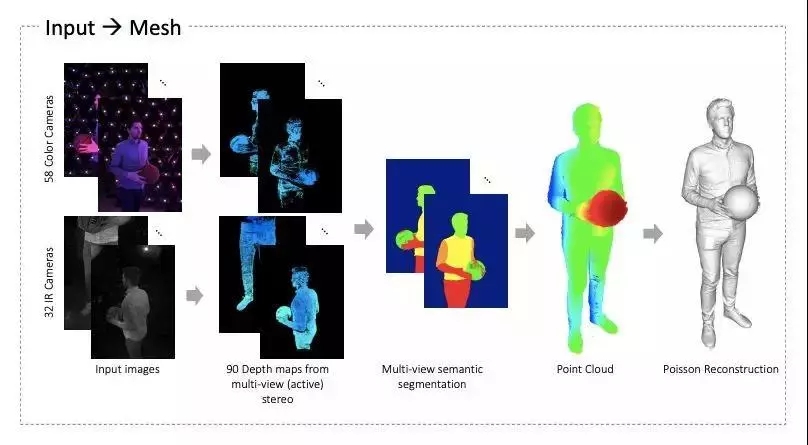
Relightables system workflow can be divided into three parts: capture, reconstruction and rendering.
The core of the system relies on a light spherical device containing a multi-view (active) stereo depth sensor. The spherical device is equipped with 331 programmable lights and 90 high-resolution 12.4MP reconstruction cameras.


The cameras used to capture the human body include 32 infrared (IR) cameras and 58 RGB cameras. Infrared sensors provide accurate and reliable 3D data, and RGB cameras capture high-quality geometric normal maps and textures. These cameras record raw video at 60Hz, and researchers alternate between two different lighting conditions based on spherical gradient illumination.

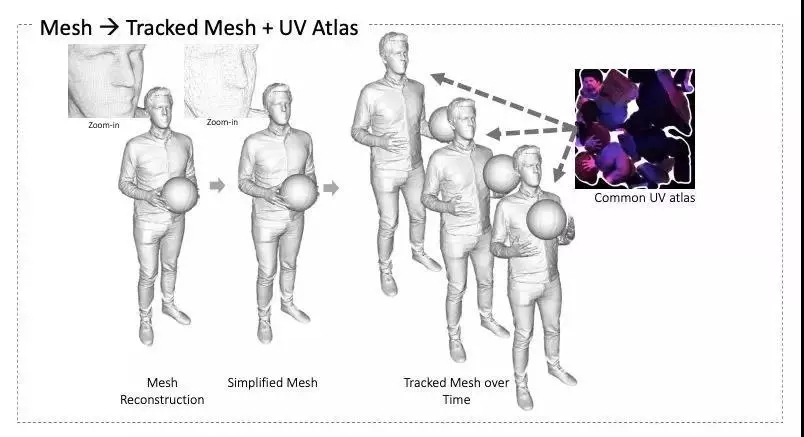
Next, the researchers upload the data to a public repository. The first stage is to generate a depth map, segmentation map, and 3D mesh for each "camera" [Kazhdan and Hoppe 2013].
They use an alignment algorithm to process the sequence of the reconstructed grid. In this way, long subsequences can share common triangulation. Researchers have proposed a new method to solve the problem of key frame selection and turn it into an MRF inference problem to solve. Each unique triangulation is parameterized into a normal 2D texture space, which can be shared with all frames that share the triangulation.
Finally, there are two gradient spherical illumination images available for each grid, from which albedo, normal, gloss, and ambient light occlusion maps can be generated. These maps are compatible with standard rendering engines and can be used to regenerate rendered images under any set lighting conditions.
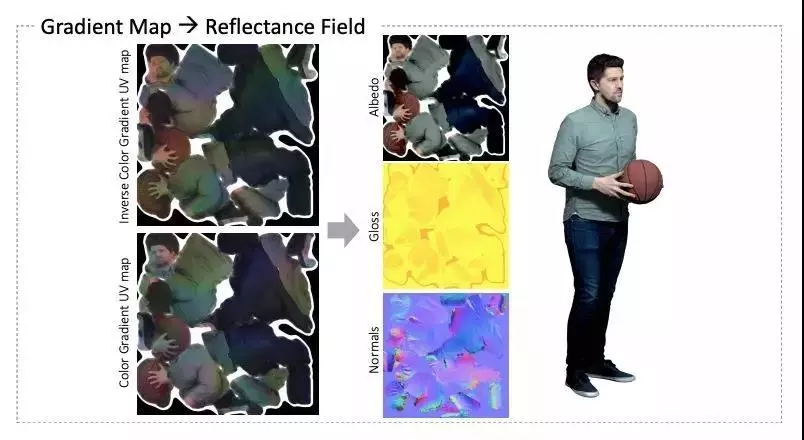

Google's new system can perfectly restore the light and shadow effects around people, making the composite image look more realistic. The captured human body can be seamlessly fused into digital scenes in the real world or in movies, games, etc. It could revolutionize the field of 3D capture technology.

